how to test for diabetic ketoacidosis Bhb test and diabetic ketoacidosis (dka)
Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) is a serious complication of diabetes that occurs when the body produces high levels of blood acids called ketones. This condition is a medical emergency and requires immediate treatment to prevent severe complications. Today, we will discuss the causes, symptoms, complications, and diagnosis of DKA.
Causes
DKA occurs when the body does not receive enough insulin. This can happen due to many reasons, including:
- Mismanagement of diabetes: If you do not monitor your blood sugar levels regularly or do not take insulin as prescribed, your body may be unable to use glucose for energy, and your body may start to break down fat for fuel, which leads to the production of ketones.
- Infections: When your body fights an infection, it can cause an increase in blood sugar levels, which may lead to DKA.
- Stress: Physical or emotional stress can also increase blood sugar levels and lead to DKA.
Symptoms
DKA symptoms usually develop quickly, within 24 hours, and may include:
- Excessive thirst
- Frequent urination
- High blood sugar level (hyperglycemia)
- High levels of ketones in the urine or blood
- Abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting
- Shortness of breath
- Fruity breath odor
- Confusion or difficulty concentrating
- Weakness or fatigue
If you experience any of these symptoms, contact your healthcare provider immediately, as DKA can be life-threatening.
Complications
If left untreated, DKA can cause severe complications, such as:
- Cerebral edema: Swelling of the brain that can cause seizures, coma, or even death. This complication is more common in children.
- Hypoglycemia: Low blood sugar levels that can lead to seizures, coma, or even death if not treated promptly.
- Cardiac arrhythmias: Irregular heartbeats that can be life-threatening.
- Pulmonary edema: Fluid buildup in the lungs that can lead to shortness of breath and difficulty breathing.
Diagnosis
If you are experiencing symptoms of DKA, your healthcare provider will perform a physical exam and order blood and urine tests to check your blood sugar levels and the presence of ketones in the urine or blood. Your healthcare provider may also perform additional tests to determine the underlying cause of DKA, such as imaging tests or cultures to check for infection.
_1541410883_40244-9.jpg) Prevention
Prevention
The best way to prevent DKA is to manage your diabetes effectively, including monitoring your blood sugar levels regularly, taking insulin as prescribed, and following a healthy diet and exercise plan. It is also essential to treat any underlying condition, such as infections or stress, promptly to prevent DKA from developing.
 Treatment
Treatment
If you are diagnosed with DKA, you will need to be treated in a hospital to prevent complications. Treatment may include:
- Intravenous fluids to replace fluid and electrolytes lost due to excessive urination
- Insulin therapy to lower blood sugar levels and reduce ketone production
- Treatment for underlying conditions, such as infections or stress
In conclusion, DKA is a serious complication of diabetes that requires immediate treatment. By managing your diabetes effectively, keeping your blood sugar levels under control, and treating any underlying conditions promptly, you can prevent DKA from developing and protect your health.
If you are searching about Ketoacidosis diagnosis, Diabetic Ketoacidosis - Labpedia.net you’ve came to the right page. We have 5 Images about Ketoacidosis diagnosis, Diabetic Ketoacidosis - Labpedia.net like Ketoacidosis diagnosis, Diabetic Ketoacidosis - Labpedia.net, BHB test and Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) - EKF Diagnostics - Stanbio and also Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) - PowerPoint Slides. Here it is:
Ketoacidosis Diagnosis, Diabetic Ketoacidosis - Labpedia.net
labpedia.netketoacidosis diabetic diagnosis diabetes ketone acidosis anion potassium labpedia mellitus metabolic
BHB Test And Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) - EKF Diagnostics - Stanbio
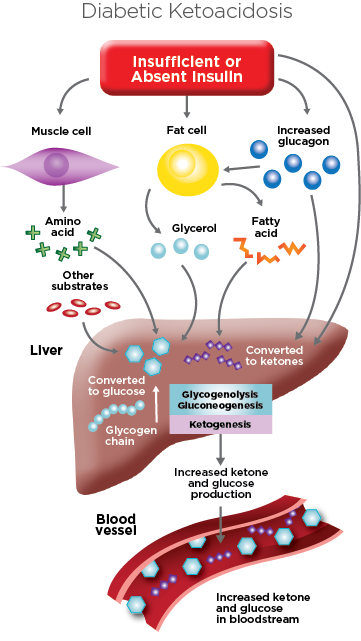 www.ekfusa.comketoacidosis hydroxybutyrate diabetic beta dka bhb test glucose blood insulin levels why liver illustration cells than
www.ekfusa.comketoacidosis hydroxybutyrate diabetic beta dka bhb test glucose blood insulin levels why liver illustration cells than
Mortality Following Diabetic Ketoacidosis Greater In T2D Vs T1D
 www.endocrinologyadvisor.comketoacidosis diabetic t2d t1d increased mortality compared sepsis ketone
www.endocrinologyadvisor.comketoacidosis diabetic t2d t1d increased mortality compared sepsis ketone
Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) - PowerPoint Slides
_1541410883_40244-9.jpg) www.myprivatetutor.mydka ketogenesis ketoacidosis diabetic hyperosmolar hyperglycemic diabetes lipolysis pathophysiology hhs nonketotic gluconeogenesis glycolysis cortisol ketogenic diets crises disambiguation epilepsy
www.myprivatetutor.mydka ketogenesis ketoacidosis diabetic hyperosmolar hyperglycemic diabetes lipolysis pathophysiology hhs nonketotic gluconeogenesis glycolysis cortisol ketogenic diets crises disambiguation epilepsy
Diabetic Ketoacidosis - Causes, Symptoms, Complications, Diagnosis
 www.medindia.netketoacidosis blood detect dka complications
www.medindia.netketoacidosis blood detect dka complications
Ketoacidosis diabetic diagnosis diabetes ketone acidosis anion potassium labpedia mellitus metabolic. Ketoacidosis blood detect dka complications. Diabetic ketoacidosis